How to Fake or Mock an API with JSON Server
Posted by Christian Weiß on January 18, 2019
Create A REST API With JSON Server
A common task for front-end developers is to simulate a backend REST service to deliver some data in JSON format to the front-end application and make sure everything is working as expected.
Of course you can setup a full backend server, e.g. by using Node.js, Express and MongoDB. However this takes some time and a much simpler approach can help to speed up front-end development time.
JSON Server is a simple project that helps you to setup a REST API with CRUD operations very fast. The project website can be found at https://github.com/typicode/json-server.
In the following you’ll lean how to setup JSON server and publish a sample REST API. Furthermore you’ll see how to use another library, Faker.js, to generate fake data for the REST API which is exposed by using JSON server.
Installing JSON Server
JSON Server is available as a NPM package. The installation can be done by using the Node.js package manager:
$ npm install -g json-server
By adding the -g option we make sure that the package is installed globally on your system.
JSON File
Now let’s create a new JSON file with name userscontacts.json. This file contains the data which should be exposed by the REST API. For objects contained in the JSON structure CRUD entpoints are created automatically. Take a look at the following sample userscontacts.json file:
{
"usercontacts": [
{
"id": 1,
"firstname": "Alex",
"lastname": "BlaBla",
"email": "alex.blabla@aol.at"
},
{
"id": 2,
"firstname": "Otto",
"lastname": "Blubb",
"email": "otto.blubb@dsl.de"
},
{
"id": 3,
"firstname": "Peter",
"lastname": "Pan",
"email": "peter.pan@neverland.com"
}
]
}
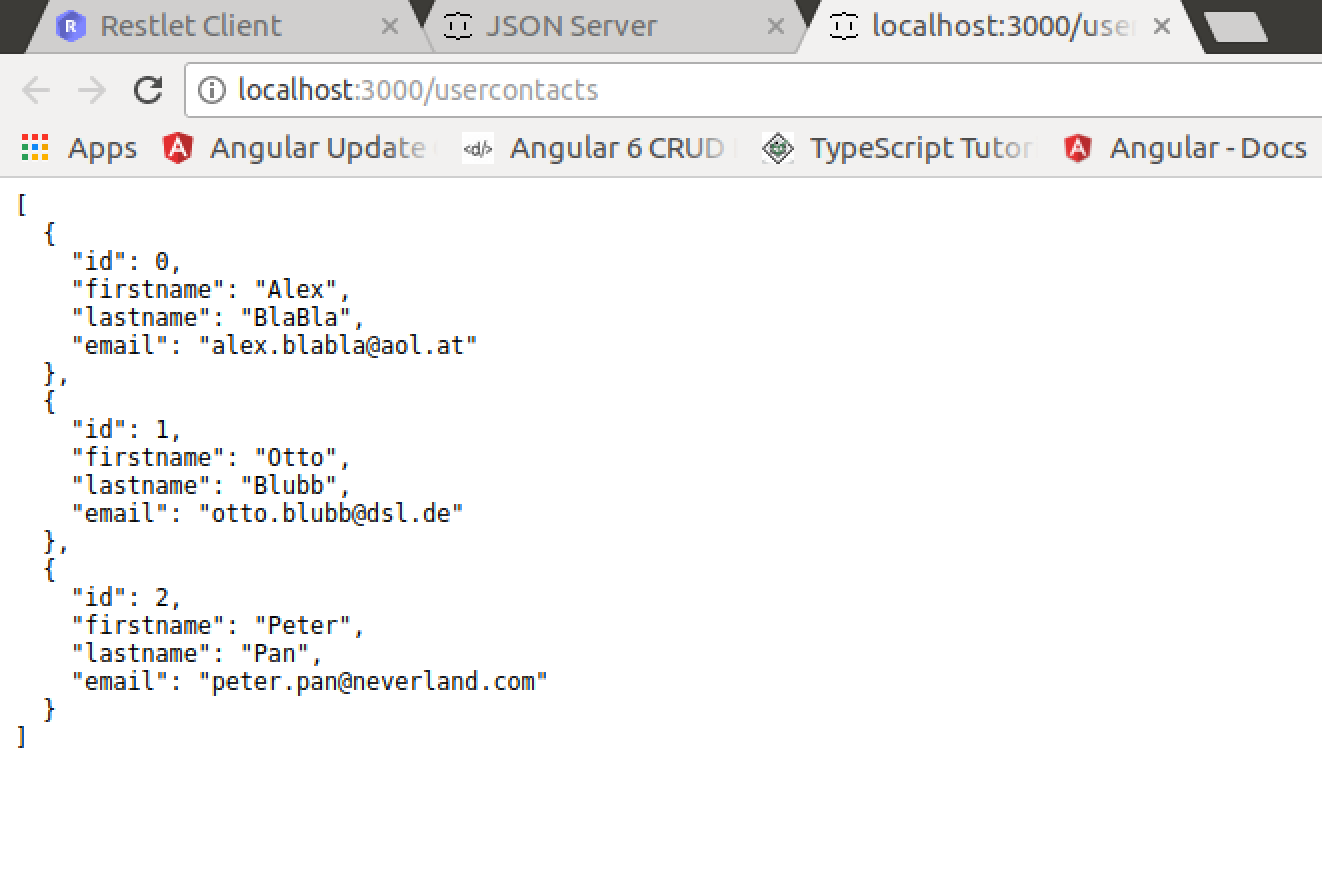
The JSON structure consists of one userscontact object which has three data sets assigned. Each userscontact object is consisting of four properties: id, firstname, lastname and email.
Running The Server
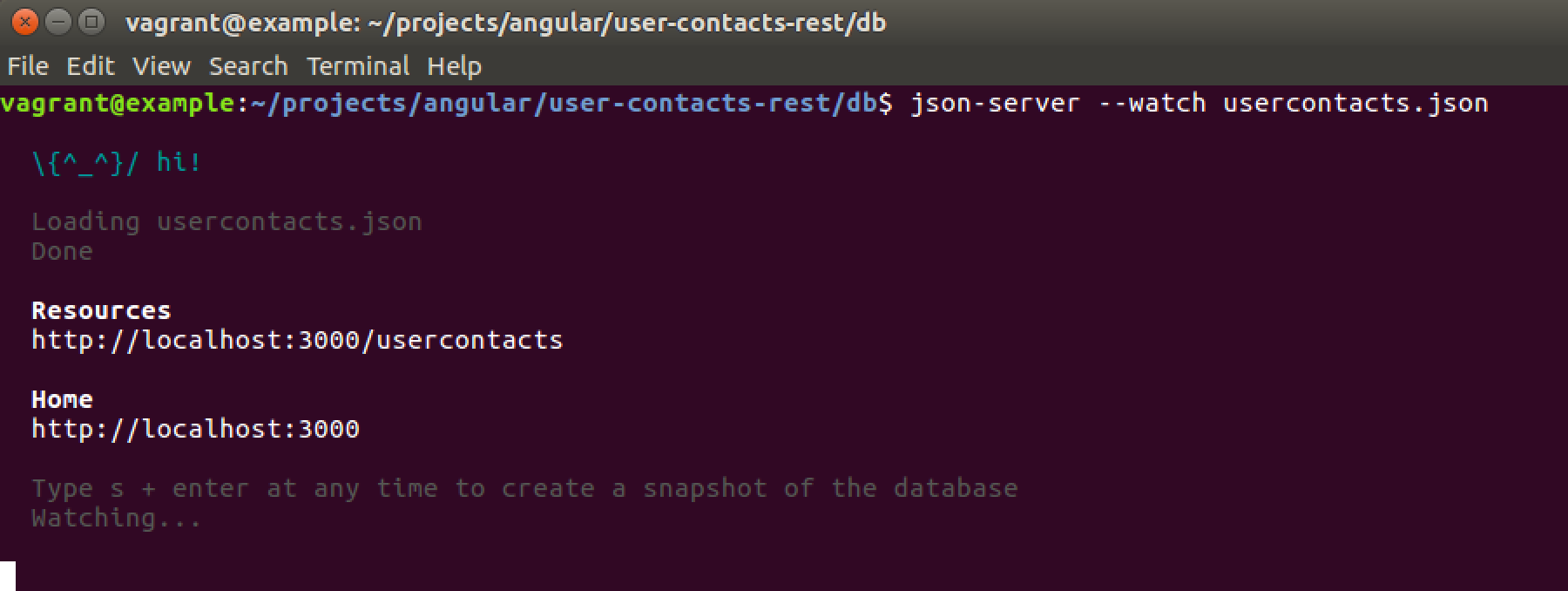
Let’s start JSON server by executing the following command:
$ json-server --watch userscontacts.json
As a parameter we need to pass over the file containing our JSON structure (userscontacts.json). Furthermore we’re using the –watch parameter. By using this parameter we’re making sure that the server is started in watch mode which means that it watches for file changes and updates the exposed API accordingly.
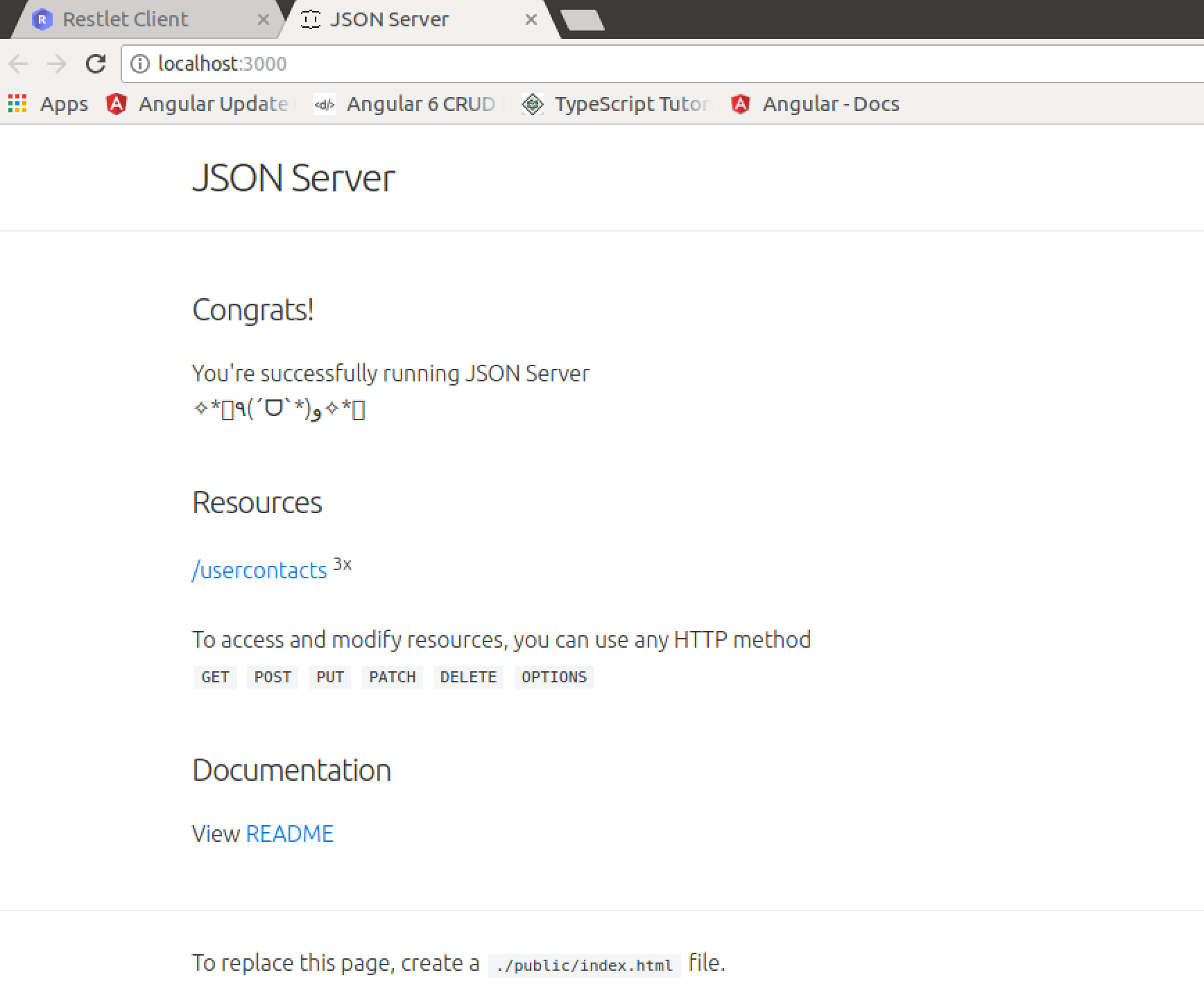
Now we can open URL http://localhost:3000/usercontacts in the browser and we’ll get the following result:
From the output you can see that the usercontacts resource has been recognized correctly. Now you can click on the usercontacts link and a HTTP GET request to http://localhost:3000/usercontacts shows the following result:
The following HTTP endpoints are created automatically by JSON server:
GET /usercontacts
GET /usercontacts/{id}
POST /usercontacts
PUT /usercontacts/{id}
PATCH /usercontacts/{id}
DELETE /usercontacts/{id}
If you make POST, PUT, PATCH or DELETE requests, changes will be automatically saved to userscontacts.json. A POST, PUT or PATCH request should include a Content-Type: application/json header to use the JSON in the request body. Otherwise it will result in a 200 OK but without changes being made to the data.
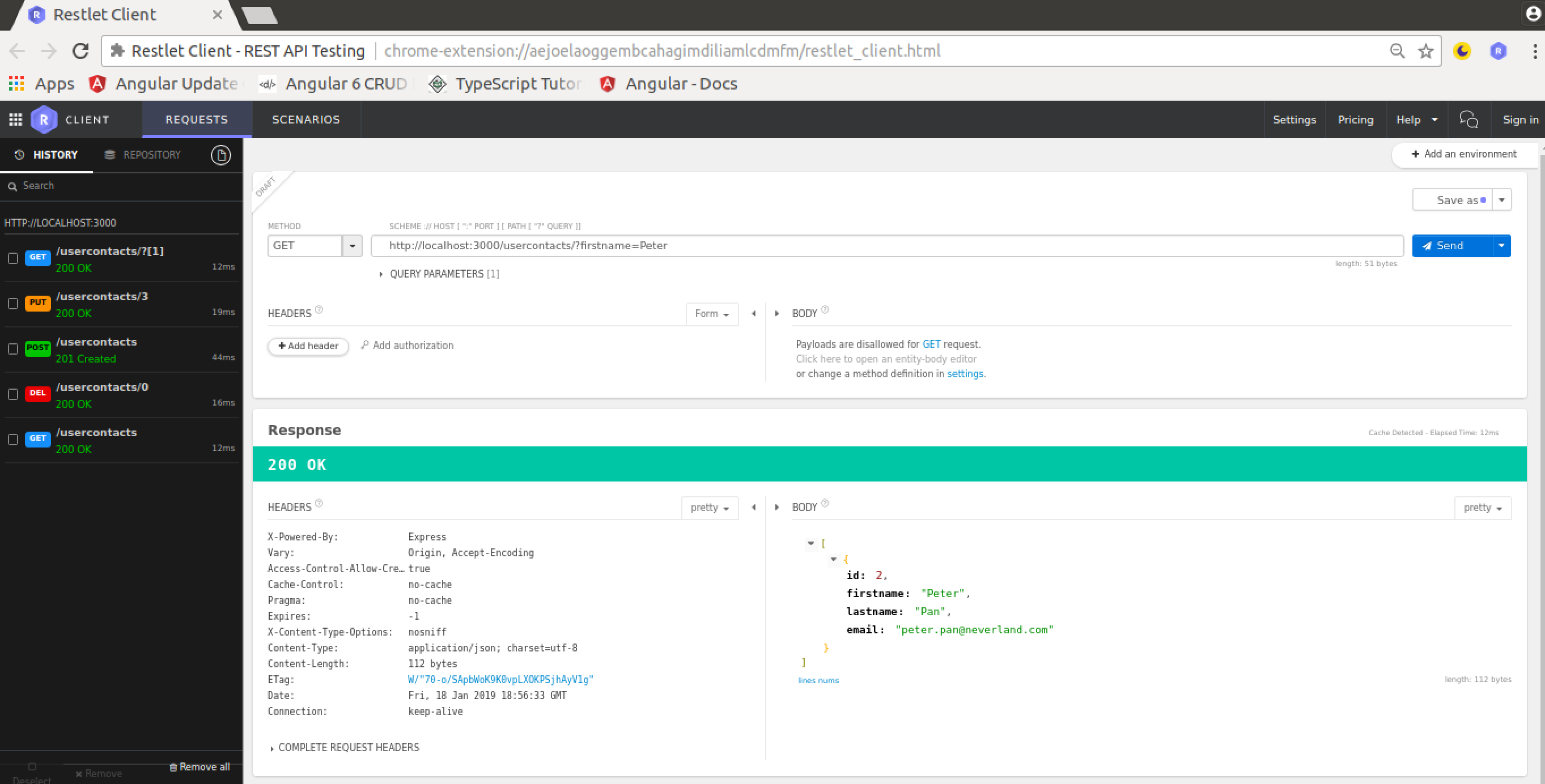
It’s possible to extend URLs with further parameter. E.g. you can apply filtering by using URL parameters like you can see in the following:
http://localhost:3000/usercontacts?firstname=Peter
This returns just one usercontacts object as a result.
For a full list of available URL parameters take a look at the JSON server documentation: https://github.com/typicode/json-server
Testing API Endpoints With REST Client
Initiating a GET request is easy by simply using the browser. For initiating other types of HTTP requests you can make use of an HTTP client tool like Postman (https://www.getpostman.com). Postman is available for MacOS, Windows and Linux. Furthermore Postman is available as a Chrome App, or one of the REST Client Browser Extensions. I use the Restlet Client
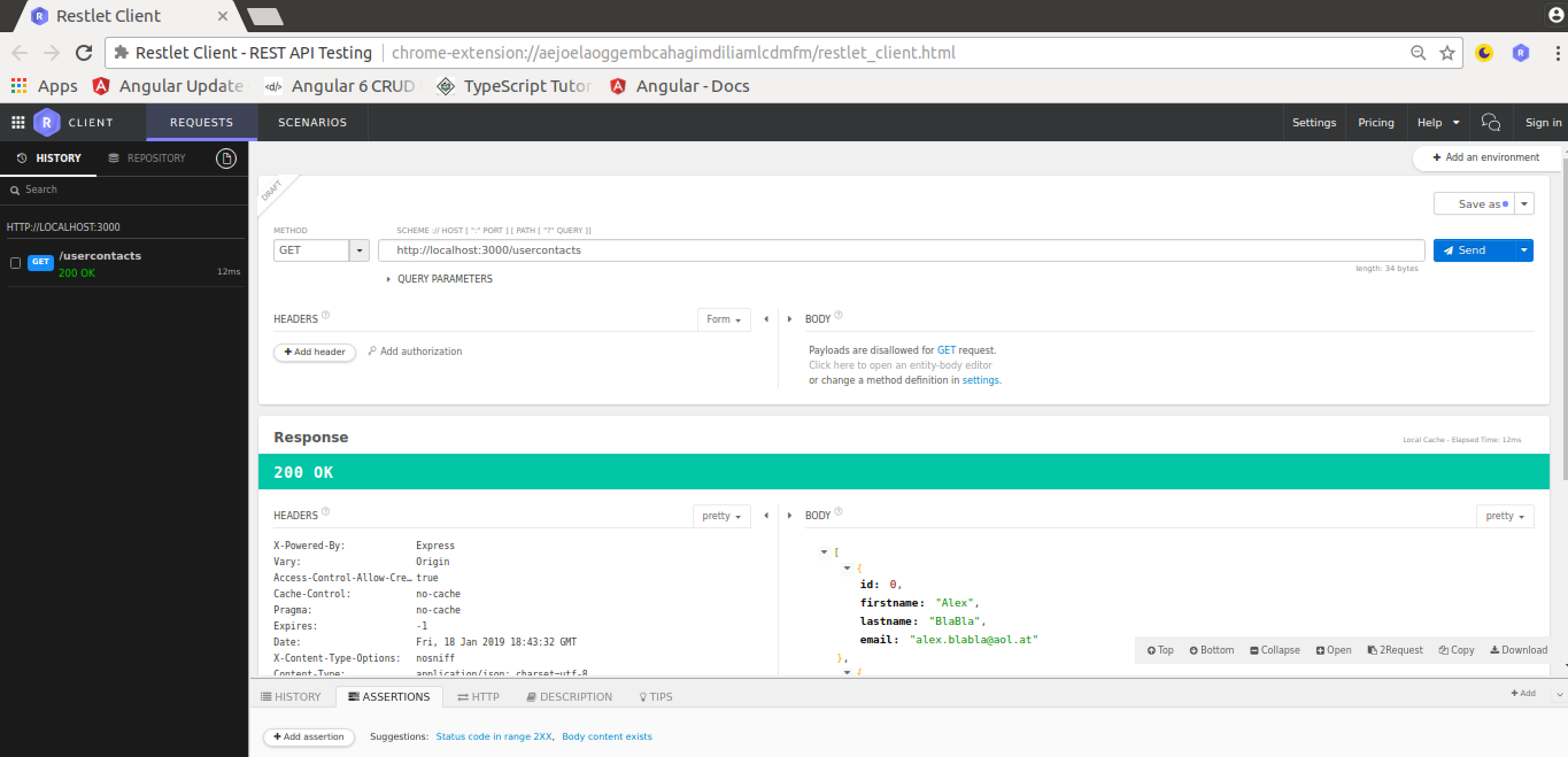
Get Request
The Restlet Client user interface is easy to use. To initiate a GET request fill out the form as you can see in the following screenshot. Click the Send button and you’ll receive the response in JSON format:
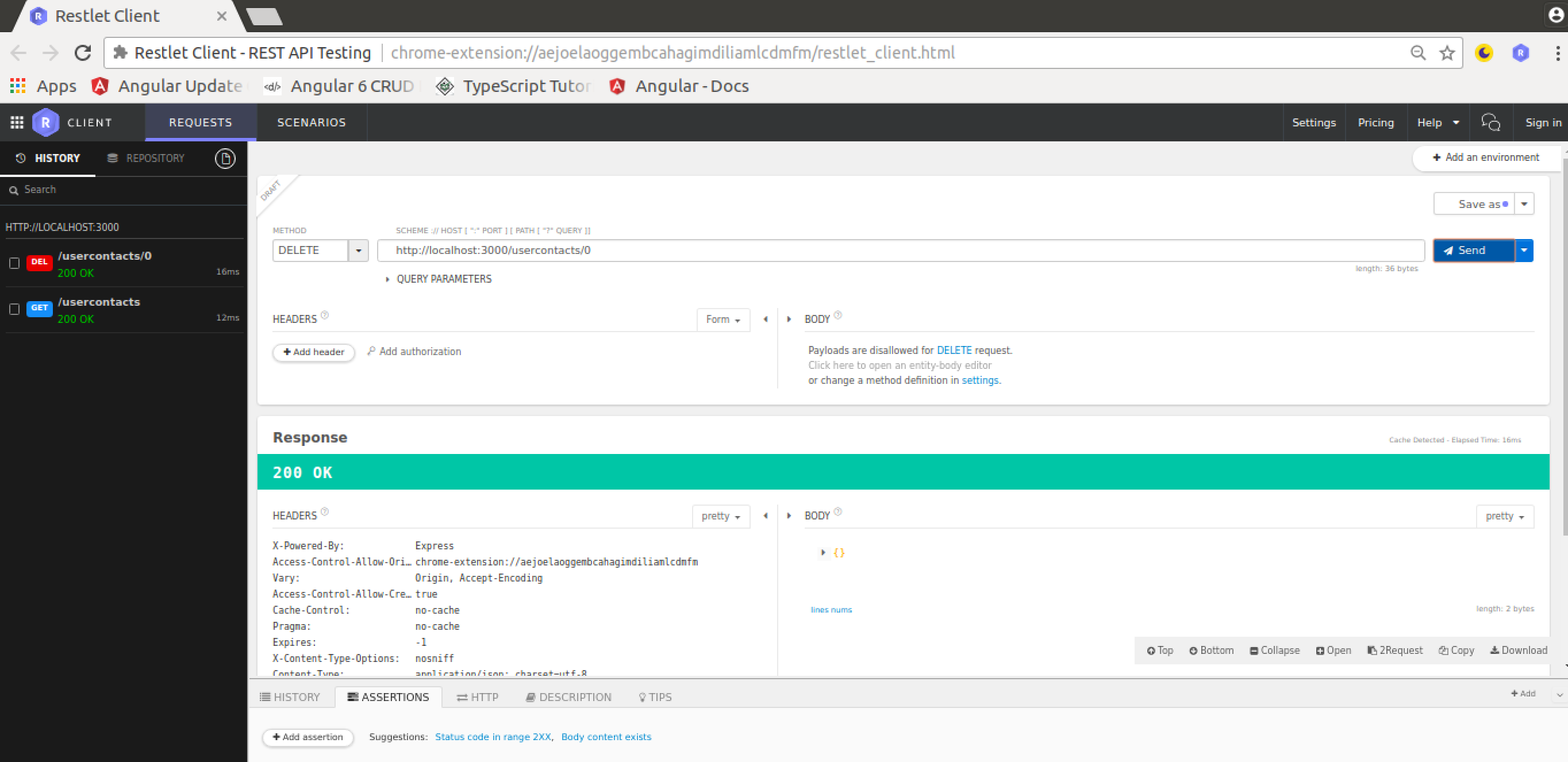
DELETE REQUEST
A corresponding delete request can be seen in the following screenshot:
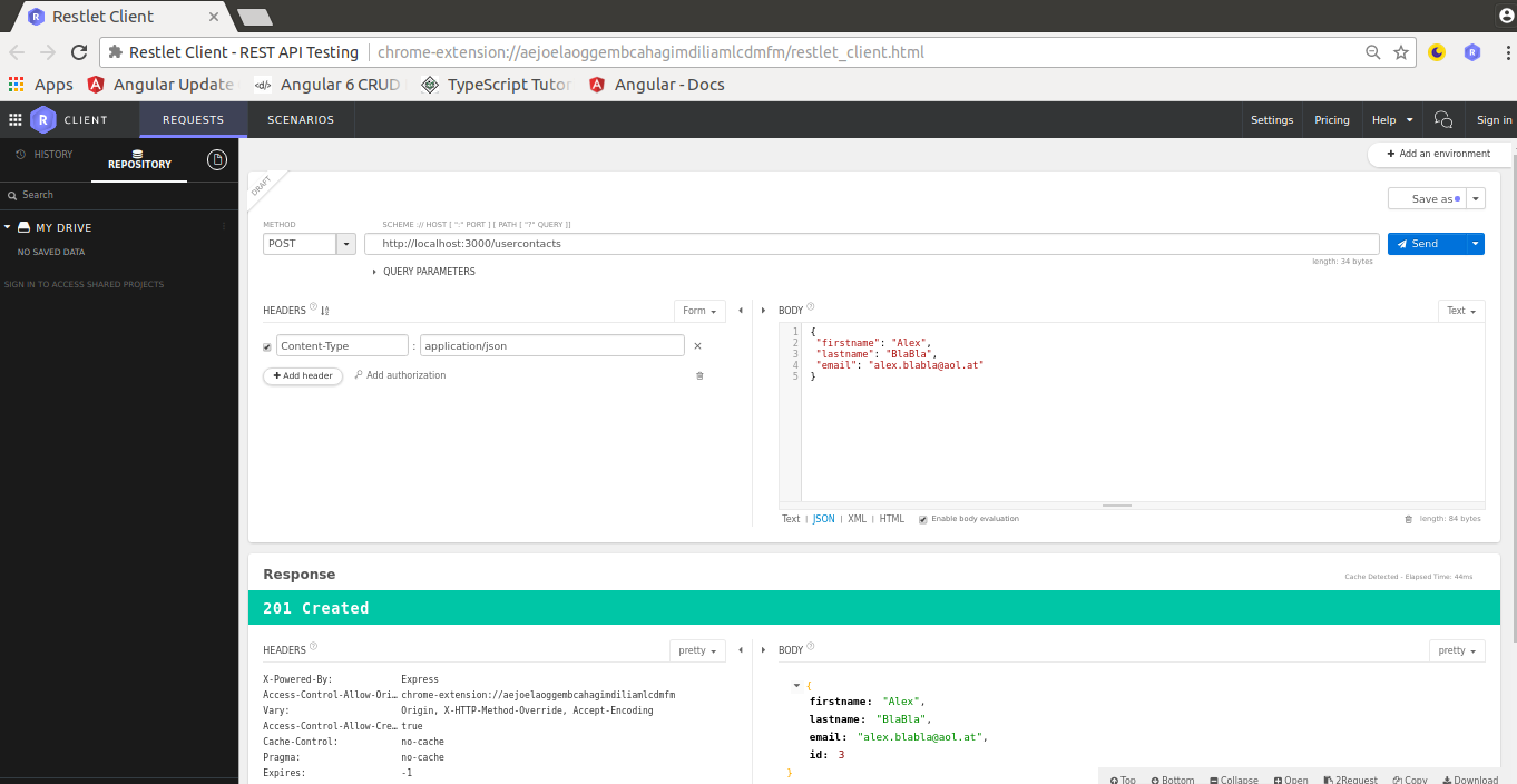
POST REQUEST
To create a new usercontact we need to perform a post request and set the body content type to JSON (application/json). The new usercontacts object is entered in JSON format in the body data section:
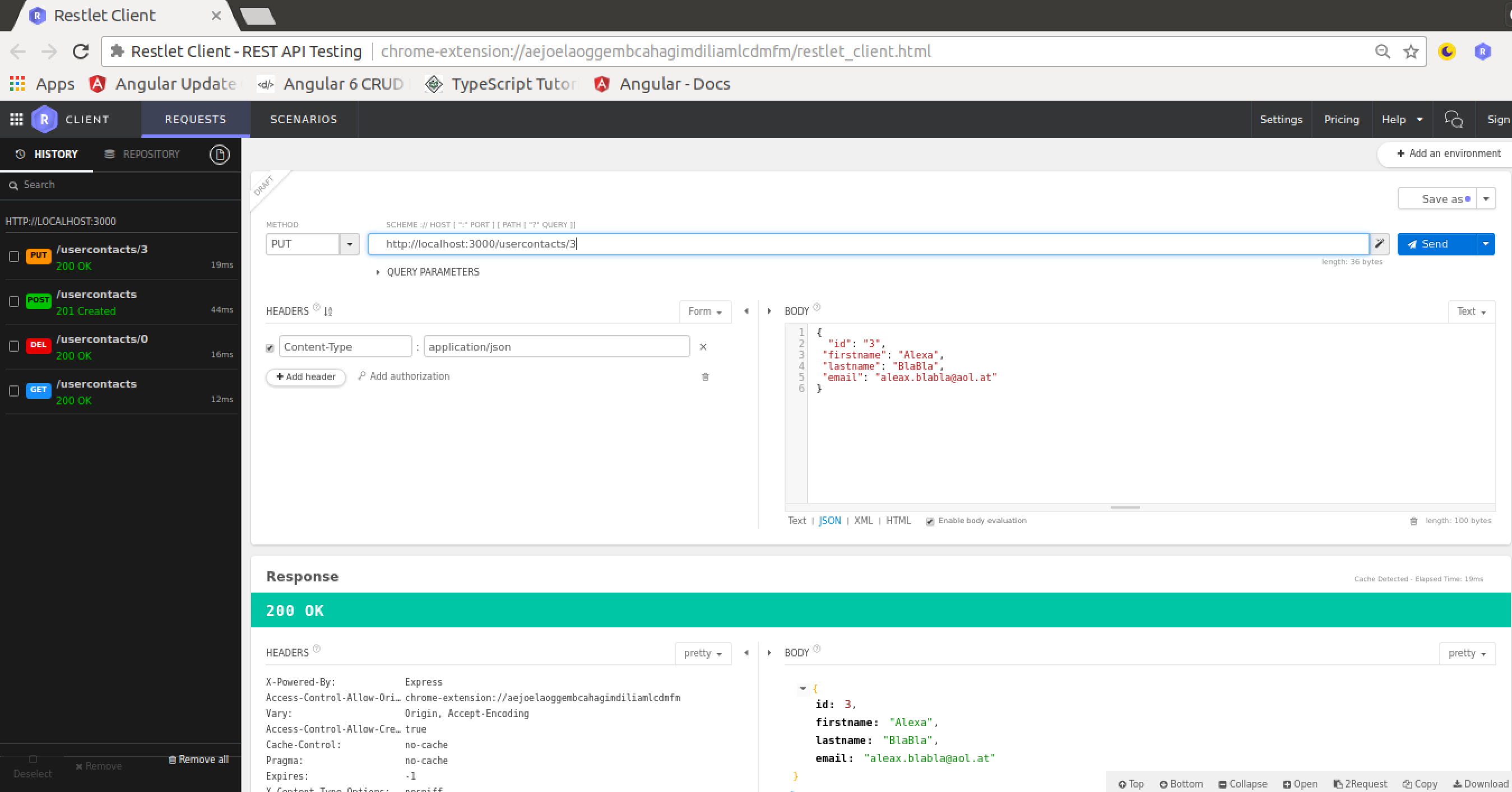
PUT REQUEST
If you want to update or change an existing usercontacts record you can use a HTTP PUT request: