Mkcert - Create SSL Certificates for Local Development
Posted by Christian Weiß on September 30, 2018
Mkcert is a simple tool which can be used in making locally trusted certificates. It doesn’t require any configuration. It is always dangerous or impossible to use certificates from real Certificate Authorities for localhost or 127.0.0.1. Even using self-signed certificates are equally not recommended as they cause trust errors.
Mkcert provides us with the best solution to this by managing its own CA. This will automatically create and installs a local CA in the system root store and generates locally-trusted certificates.
Installation
Warning: the
rootCA-key.pemfile that mkcert automatically generates gives complete power to intercept secure requests from your machine. Do not share it.
Github Repo
Linux
On Linux, first install certutil.
sudo apt install libnss3-tools
-or-
sudo yum install nss-tools
-or-
sudo pacman -S nss
Then you can install using Linuxbrew
brew install mkcert
Getting Start
Open a terminal and use the following command:
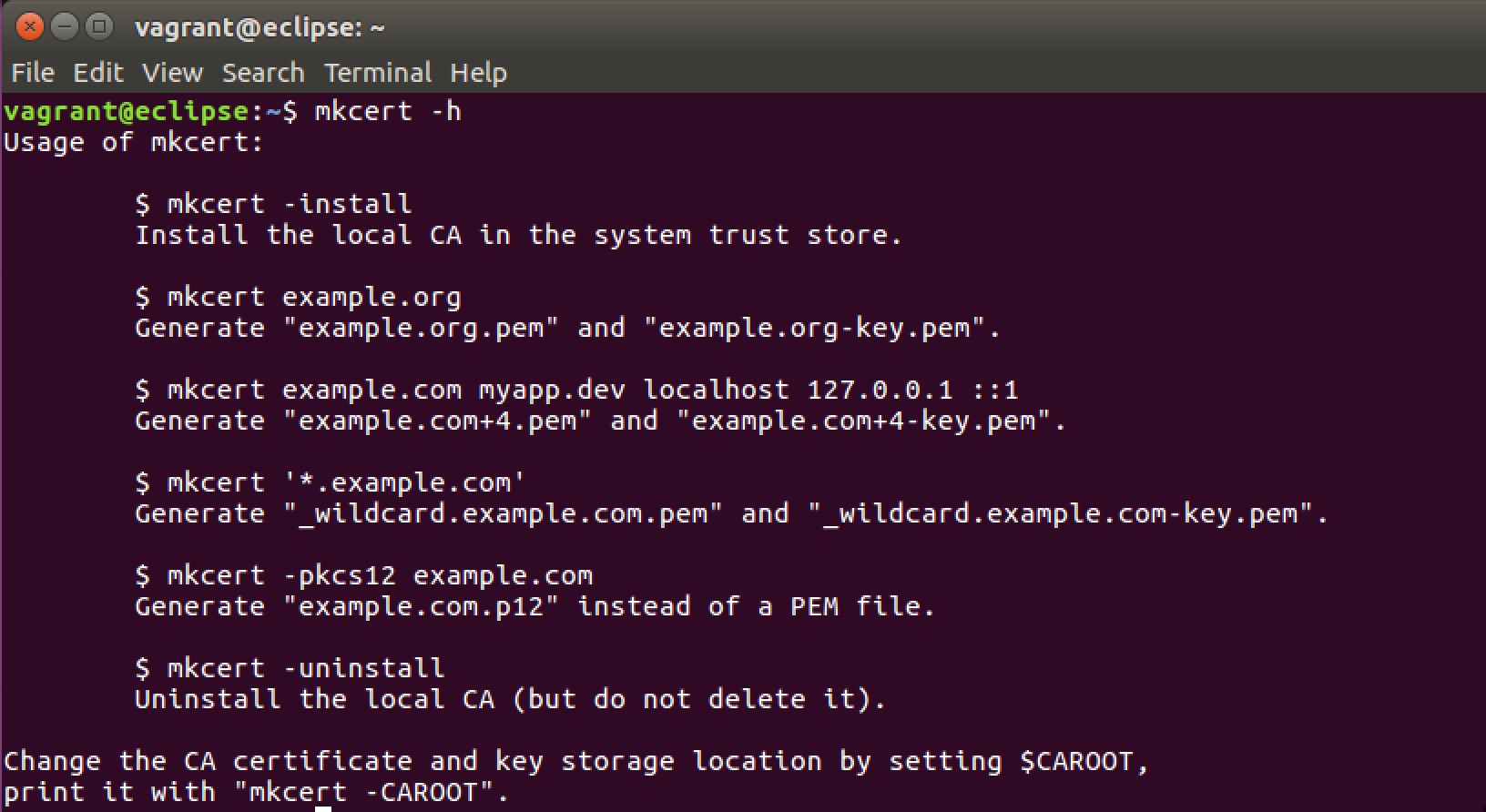
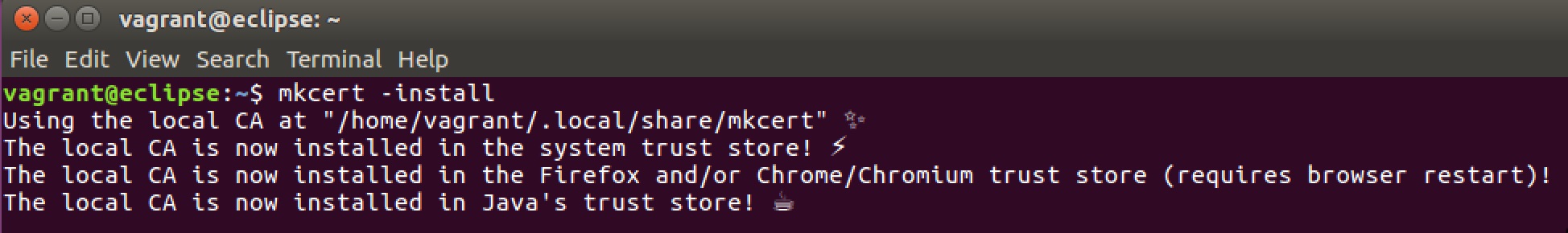
mkcert -install
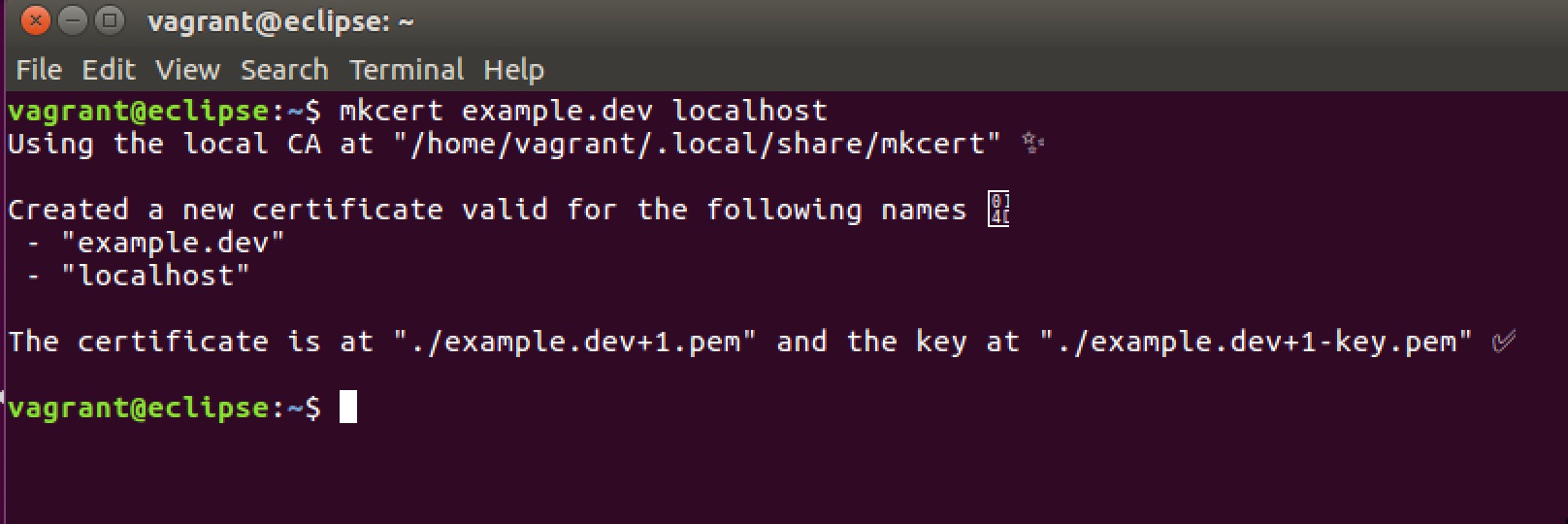
Create a Certificate
mkcert example.dev localhost
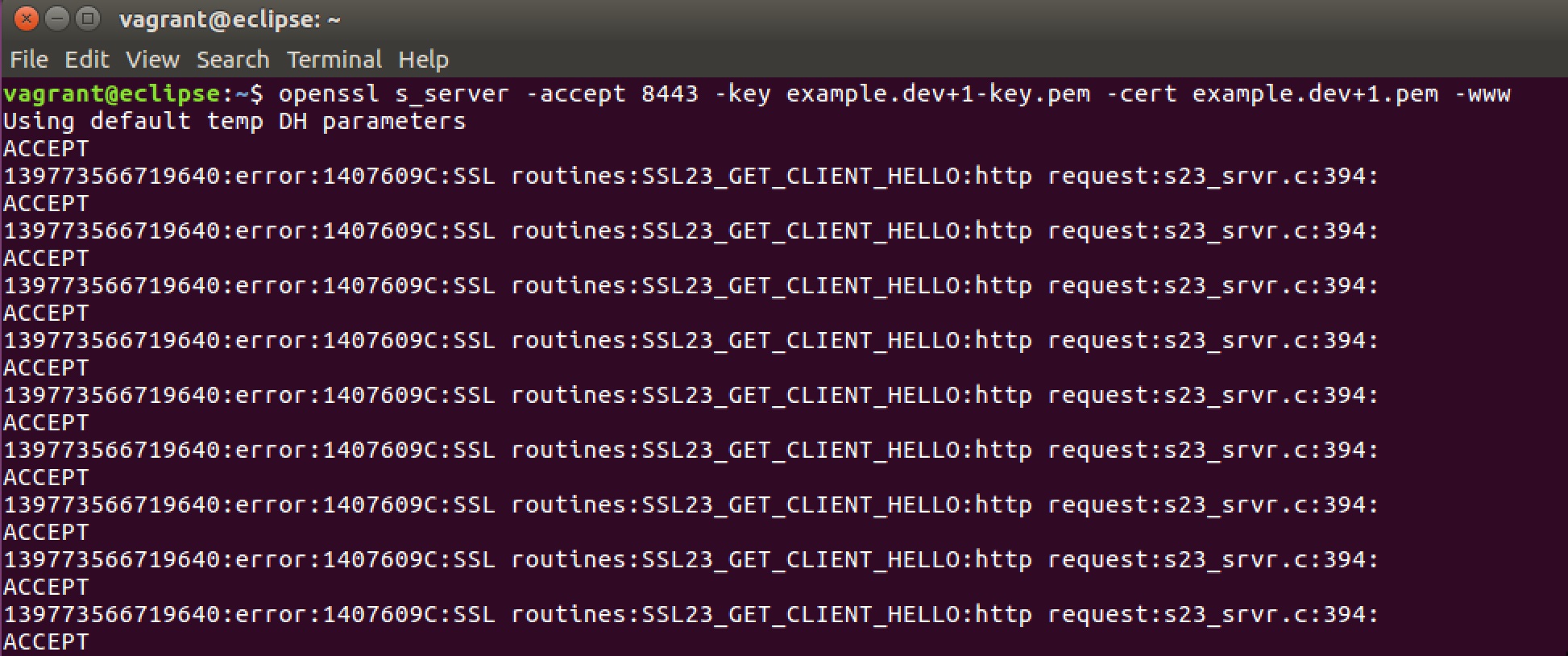
Start a test server with openssl s_server and the mkcert certificates
openssl s_server -accept 8443 -key example.pev+1-key.pem -cert example.pev+1.pem -www
Open your browser and start https://localhost:8443
Supported root stores
mkcert supports the following root stores:
- macOS system store
- Windows system store
- Linux variants that provide either
update-ca-trust(Fedora, RHEL, CentOS) orupdate-ca-certificates(Ubuntu, Debian) ortrust(Arch)
- Firefox (macOS and Linux only)
- Chrome and Chromium
- Java (when
JAVA_HOMEis set)
Changing the location of the CA files
The CA certificate and its key are stored in an application data folder in the user home. You usually don’t have to worry about it, as installation is automated, but the location is printed by mkcert -CAROOT.
If you want to manage separate CAs, you can use the environment variable $CAROOT to set the folder where mkcert will place and look for the local CA files.
Installing the CA on other systems
Installing in the trust store does not require the CA key, so you can export the CA certificate and use mkcert to install it in other machines.
- Look for the
rootCA.pemfile inmkcert -CAROOT - copy it to a different machine
- set
$CAROOTto its directory - run
mkcert -install
Remember that mkcert is meant for development purposes, not production, so it should not be used on end users’ machines, and that you should not export or share rootCA-key.pem.